Should AI imitate cognitive mechanisms?


- Planes do not fly like birds
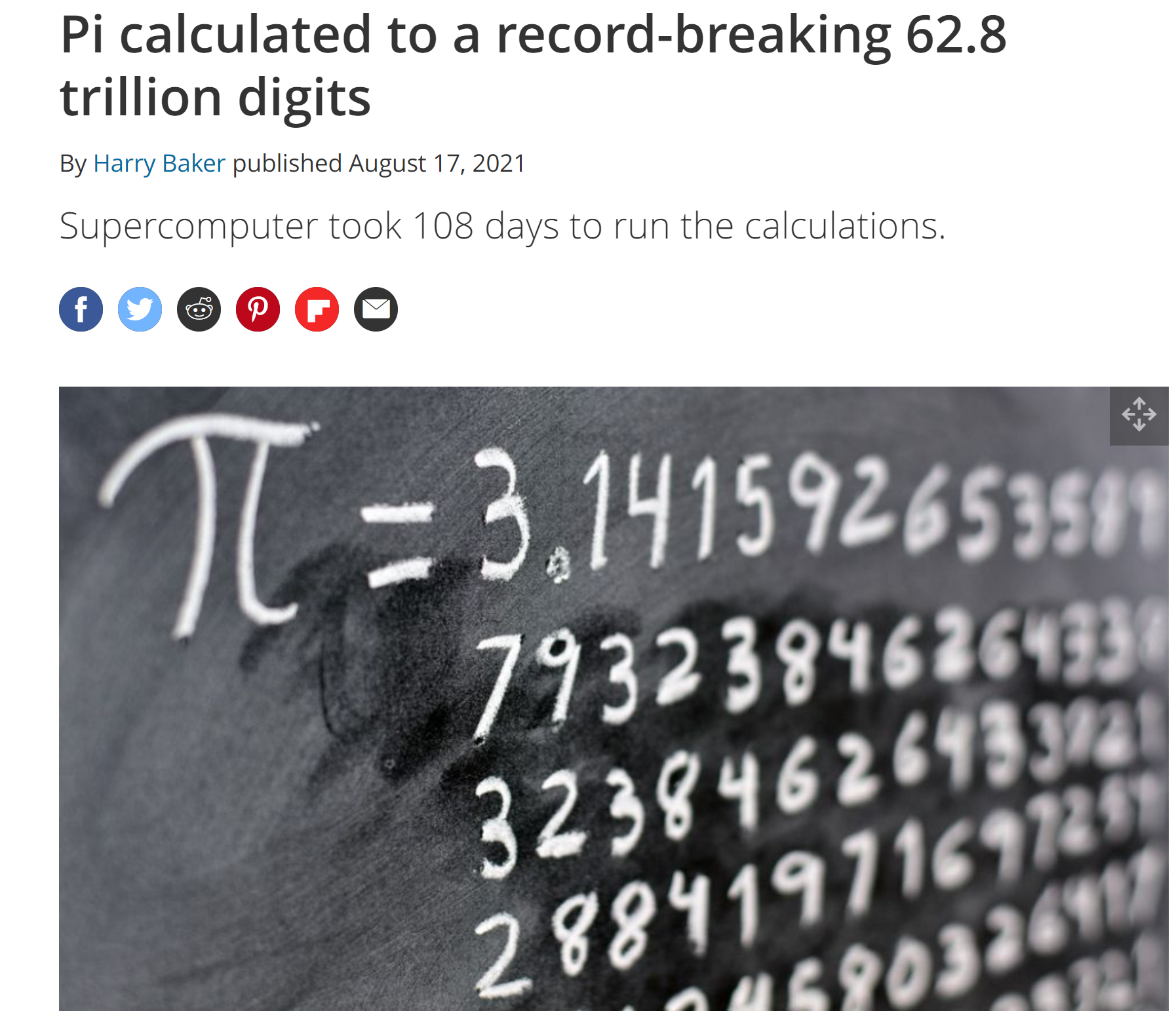
- Computers can retrieve trillions of π’s decimals
- Computers can learn Chinese just by reading Chinese texts

AI relies on data


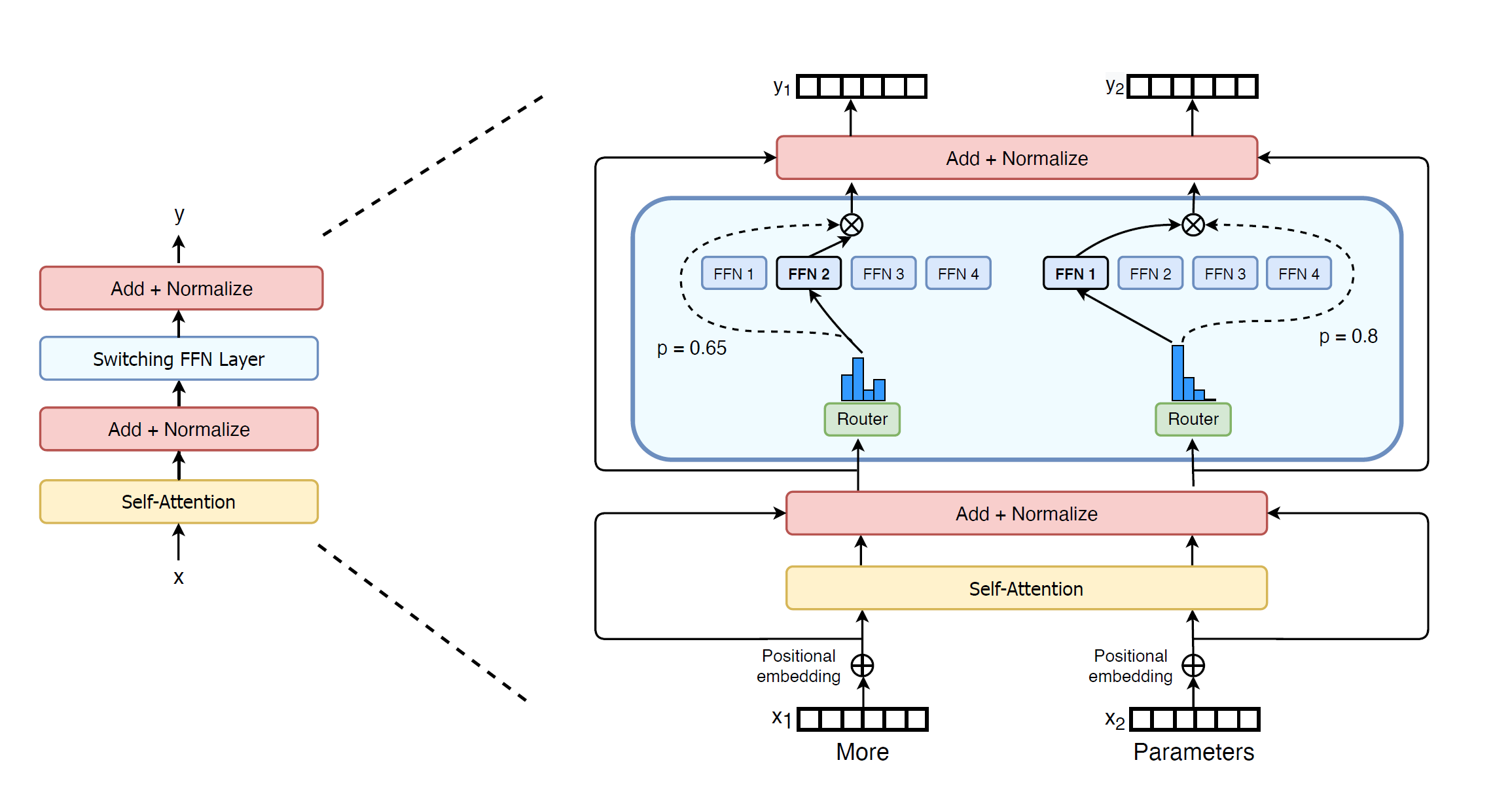
And it works!
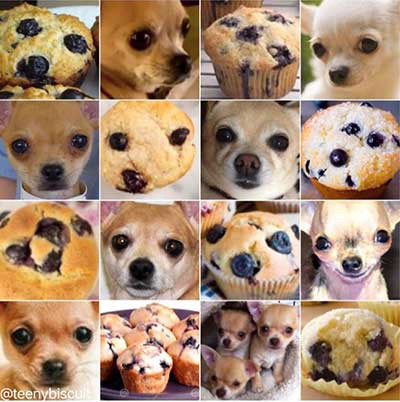

Krizhevsky, A., et al. (2012). Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. NIPS 2012, 1097-1105.

Silver, D. et al., (2017). Mastering the game of go without human knowledge. Nature, 550 (7676), 354-359.
And it works!


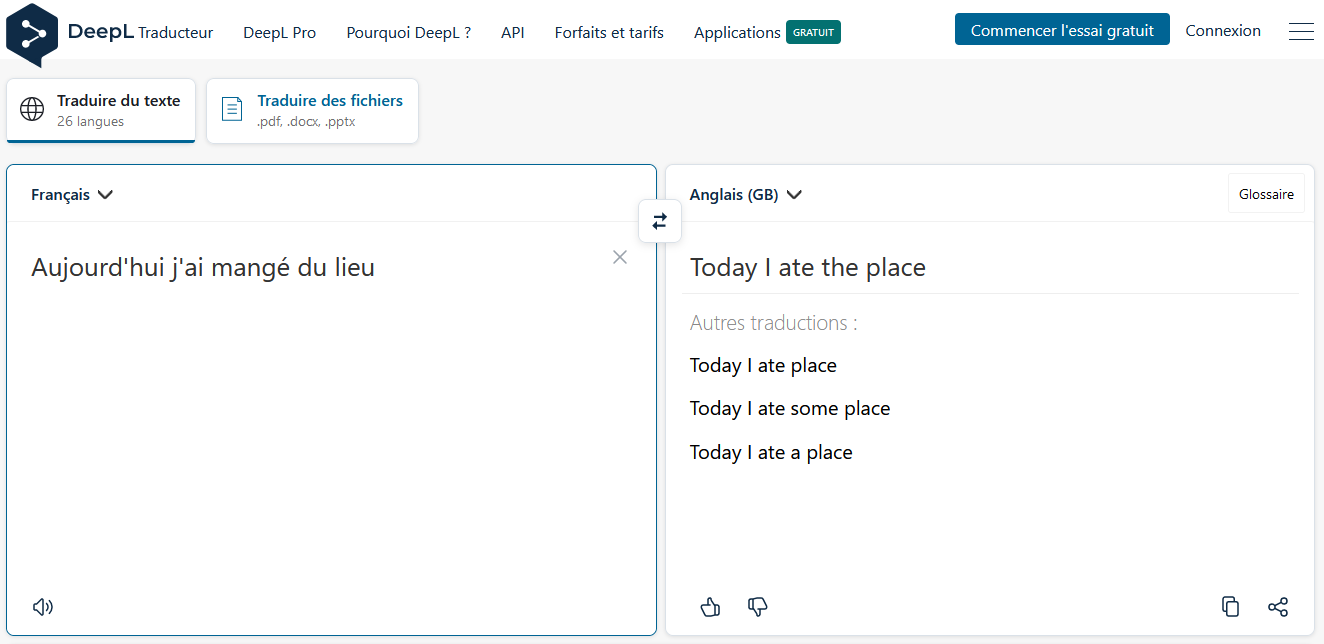
Now what’s the problem?
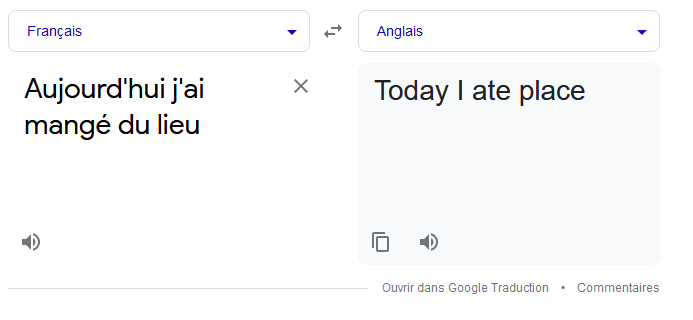

Now what’s the problem?
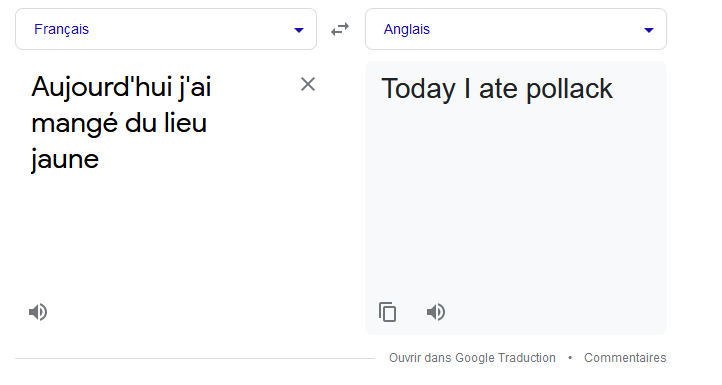
Now what’s the problem?
Now what’s the problem?
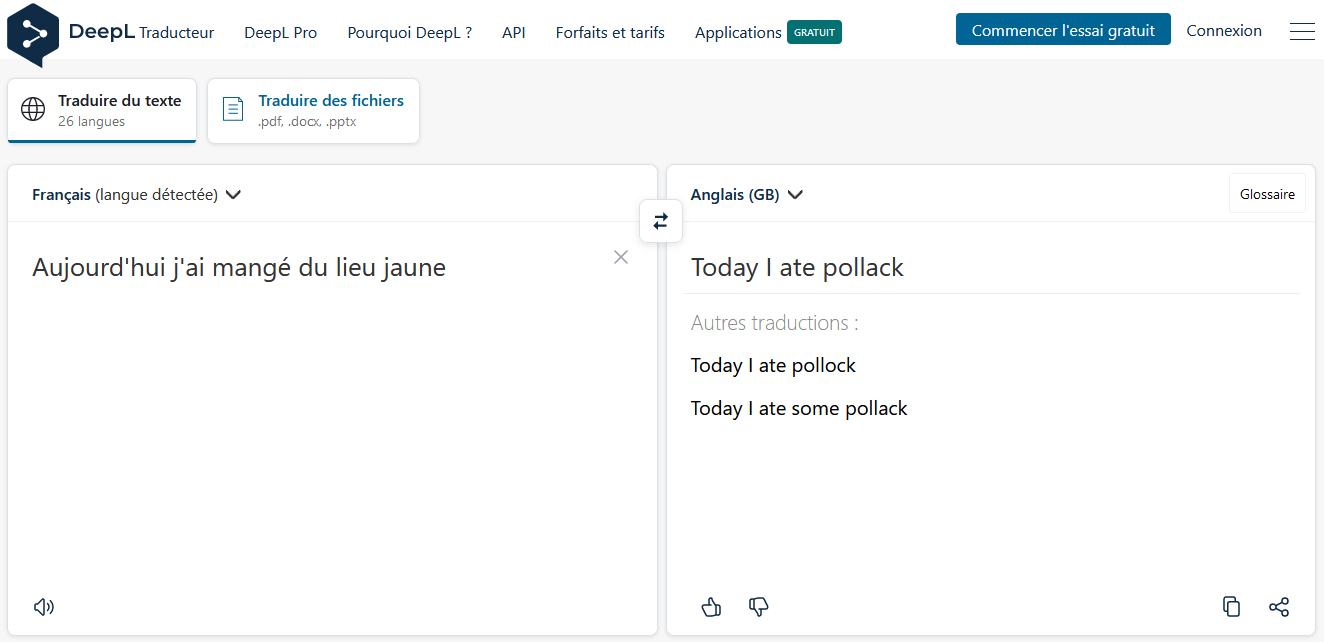
Now what’s the problem?
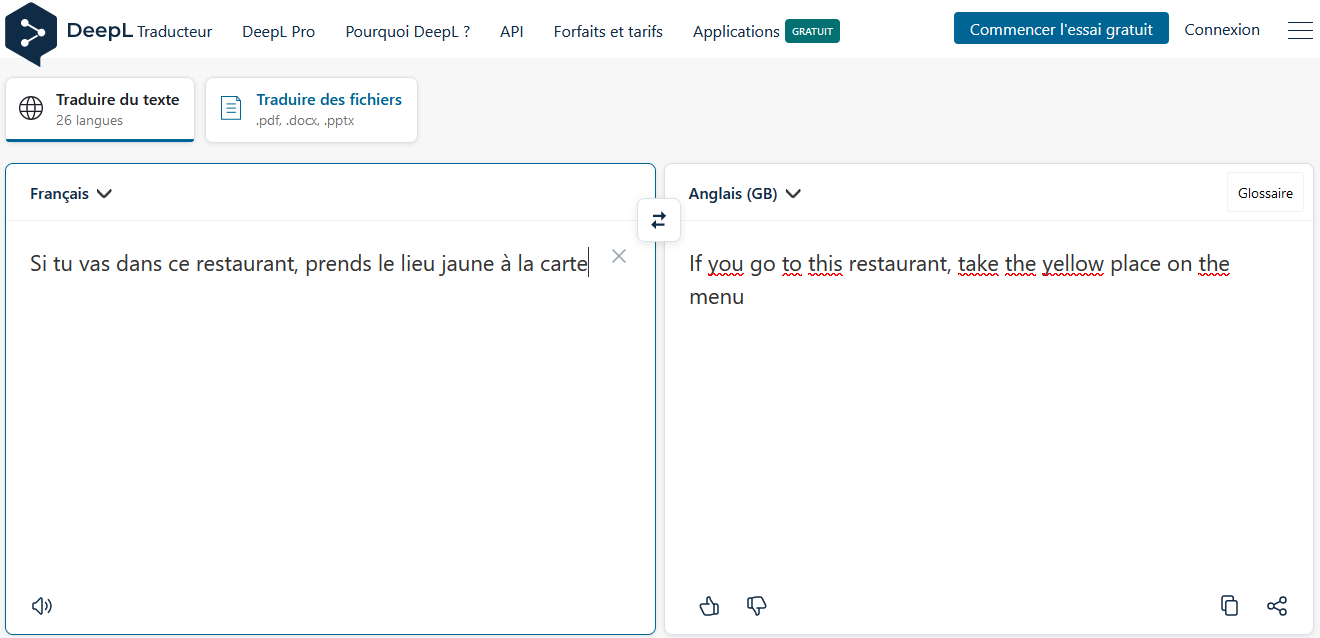
Now what’s the problem?
- "The senators were helped by the managers." → The senators helped the managers.
- "The managers heard the secretary resigned." → The managers heard the secretary.
- "If the artist slept, the actor ran." → The artist slept
- "The doctor near the actor danced." → The actor danced.
McCoy, R. T., Pavlick, E. & Linzen, T. (2019).
Right for the wrong reasons: Diagnosing syntactic heuristics in natural language inference. ArXiv:1902.01007.
Now what’s the problem?

Marcus, G. & Davis, E. (2020). GPT-3, Bloviator: OpenAI’s language generator has no idea what it’s talking about.
MIT Technology review

Mitchell, M. (2021). Why AI is harder than we think.
ArXiv:2104.12871.
none of these predictions has come true.
Now what’s the problem?

on generic contexts. Intelligent systems should be able to adapt to specific contexts.
Now what’s the problem?

| Bring me the little |
little bacterium
little book little galaxy |
| green | #00FF00 |
| book that is to the right of |
to the right of the lamp
to the right of the bus to the right of the Eiffel Tower |
| the lamp on |
The car is on the road.
The city is on the map. The fly is on the ceiling. |
| my desk. |
She is sitting on my desk.
Go to the reception desk. A desk at the Foreign Office. |
Why is statistical AI limited?
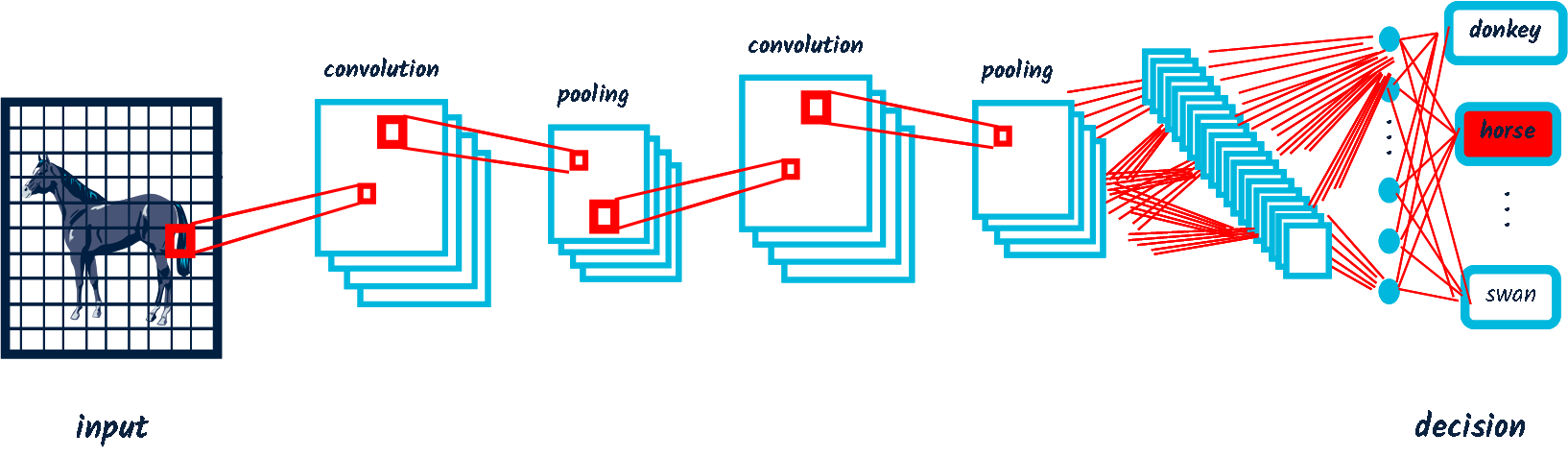
- (Deep) neural networks are continuous machines.
- They learn how to interpolate between examples.

|

|
0.817044 |

|

|
0.630777 |

|

|
0.223796 |

|

|
0.110613 |

|

|
0.087145 |

|

|
0.076637 |

|

|
0.027321 |
Why is statistical AI limited?
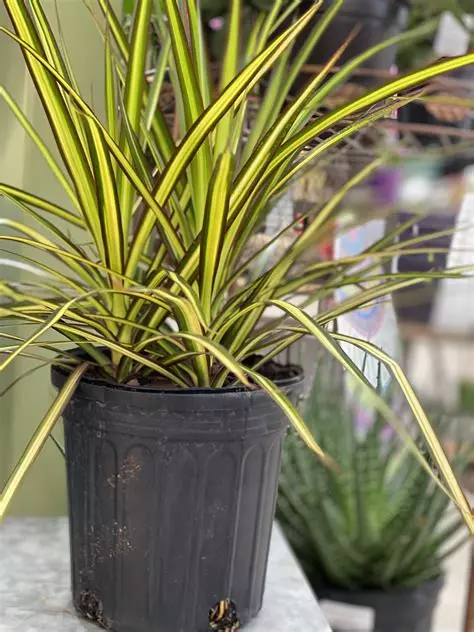
- A trivial example
that are particularly green. The only thing to learn is the "green" threshold. →
Quite magically,
• small modifications would not alter the decision.
• Resembling plants will be in the same category. This "magic" results from continuity.
Why is statistical AI limited?

- (Deep) neural networks are continuous machines.
- They learn how to interpolate between examples.
- DNN learn to pay attention to relevant features, but they remain interpolation machines.
Why is statistical AI limited?
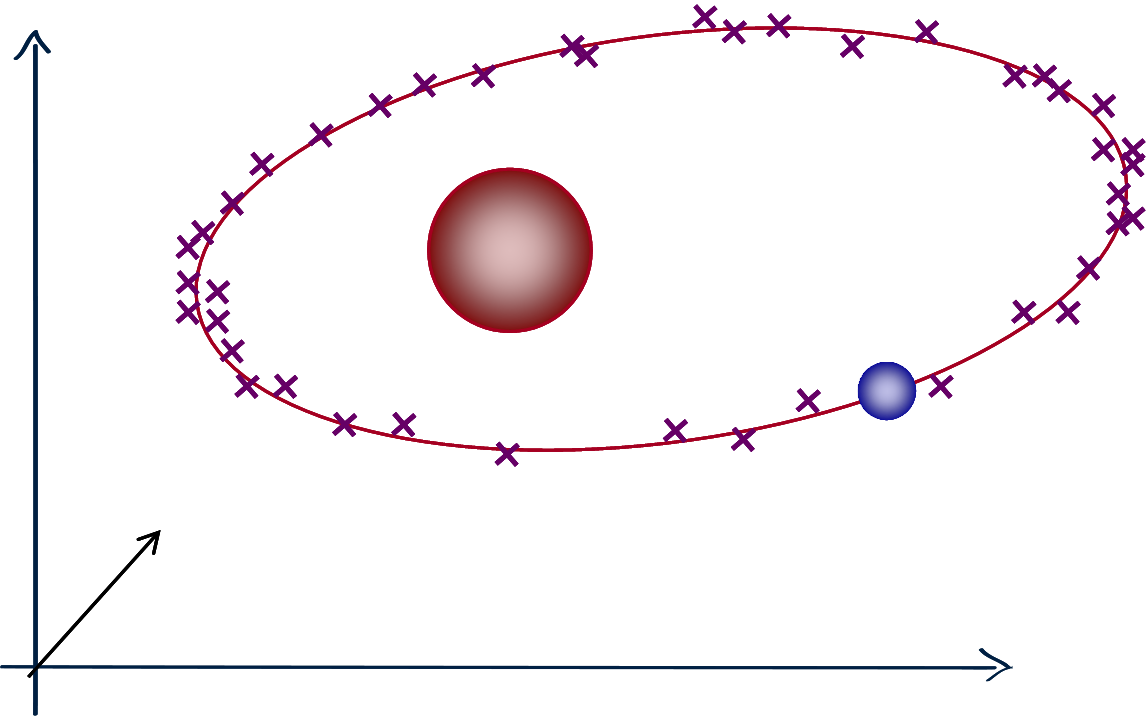
Why is statistical AI limited?
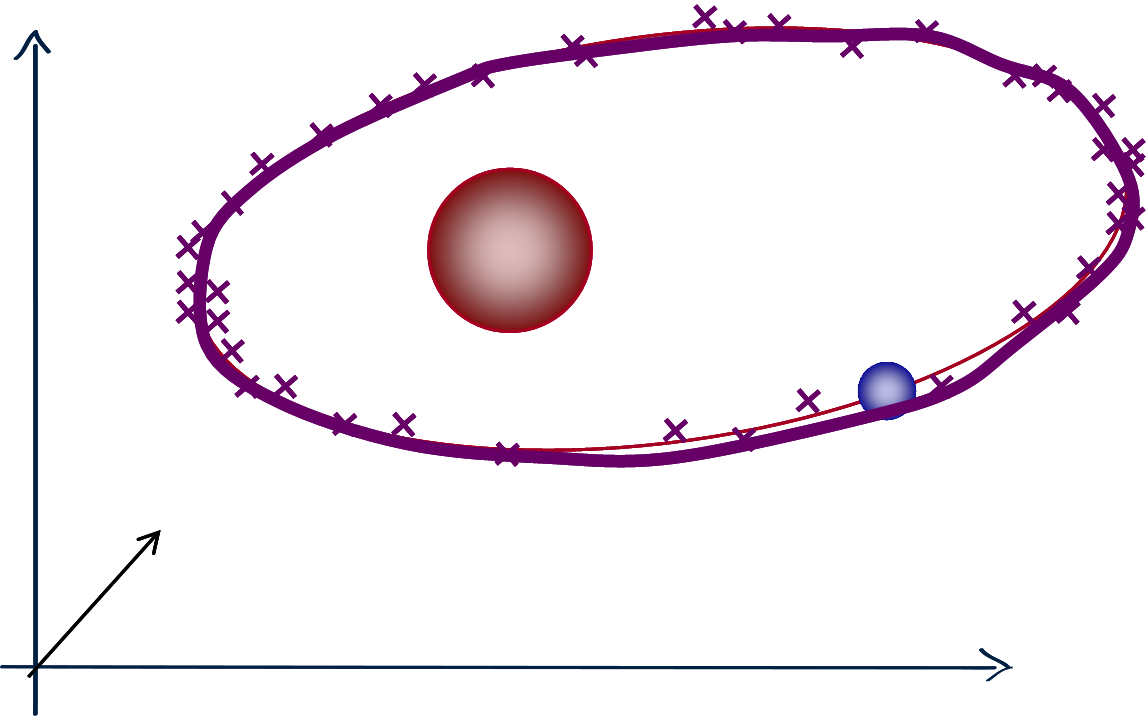
Mere interpolation
cannot abstract an ellipse.$$ \frac{x^2}{a^2} + \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 $$
Why is statistical AI limited?

Neural nets are essentially
"guessing machines"!

Can we do better?
Intelligent behavior must be computed in part
on the fly!
to be intelligent.
Some cognitive "mechanisms"
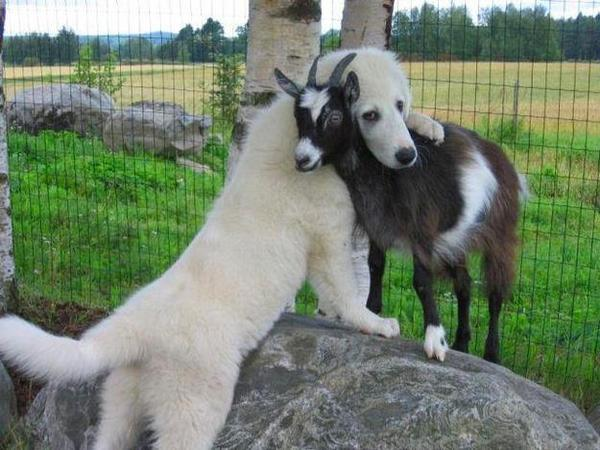
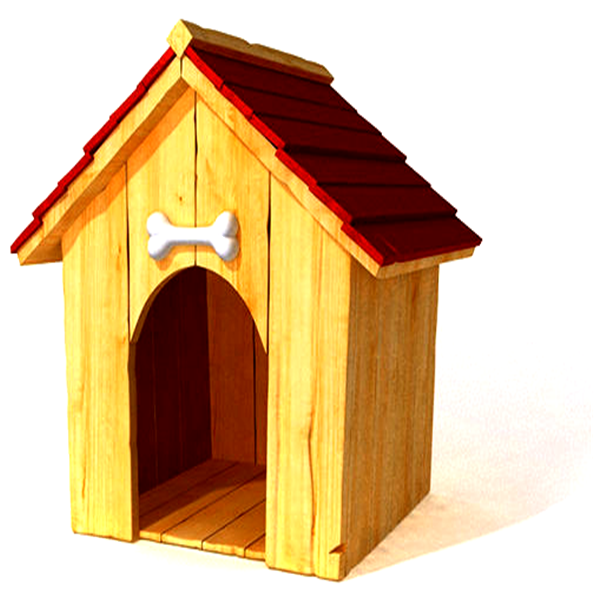


Syntax
the dog was in the doghouse. The fact that it barked revealed
that the dog was in the doghouse.
Chomsky, N. (1975). Reflections on language. New York: Pantheon Books.
Crain, S. (1991). Language acquisition in the absence of experience. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 14 (4), 597-650.
Some cognitive "mechanisms"
Syntax
the dog was in the doghouse. The fact that it barked revealed
that the dog was in the doghouse.
Some cognitive "mechanisms"
Aspect
 Elle n’est pas toujours malade ↔ elle n’est toujours pas malade
Elle n’est pas toujours malade ↔ elle n’est toujours pas malade

Pulman, S. G. (1997). Aspectual shift as type coercion.
Transactions of the Philological Society, 95 (2), 279-317.
Munch, D. & Dessalles, J.-L. (2012). Inferring aspectuality on French sentences:
a minimalist approach. CogSci-2012, 2055-2060.
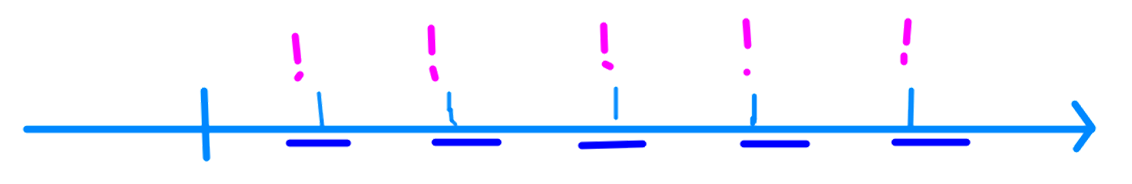
Some cognitive "mechanisms"
Aspect

Some cognitive "mechanisms"
Aspect
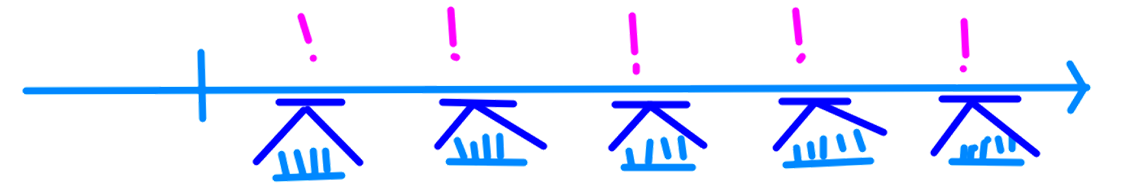
Some cognitive "mechanisms"
Aspect
Some cognitive "mechanisms"
Contrast

Some cognitive "mechanisms"
Contrast
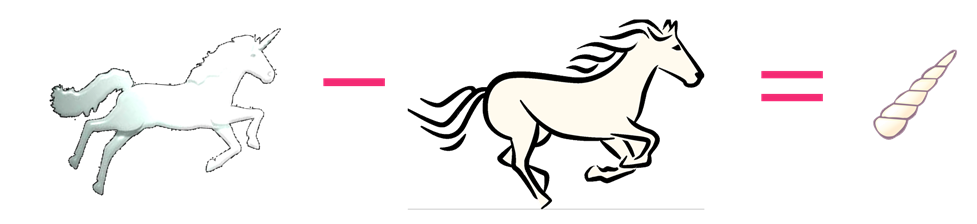
Gärdenfors, P. (2014). The geometry of meaning - Semantics based on conceptual spaces. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. |
Dessalles, J.-L. (2015). From conceptual spaces to predicates. In F. Zenker & P. Gärdenfors (Eds.), Applications of conceptual spaces: The case for geometric knowledge representation, 17-31. Dordrecht: Springer. |
Some cognitive "mechanisms"
Simplicity
- IQ test
$$ n^{*n} $$
122333444455555 The most intelligent continuation minimizes overall complexity. complexity = size (in bits) of the shortest description.
Solomonoff, R. J. (1964). A Formal Theory of Inductive Inference. Information and Control, 7 (1), 1-22.
Some cognitive "mechanisms"
Simplicity
- Analogy
rosa → rosam
vita → . . .
Some cognitive "mechanisms"
Simplicity
- Analogy
rosa → rosam
vita → vitam
Murena, P.-A., Al-Ghossein, M., Dessalles, J.-L. & Cornuéjols, A. (2020). Solving analogies on words based on minimal complexity transformation. IJCAI, 1848-1854.
Dessalles, J.-L. (2008). La pertinence et ses origines cognitives - Nouvelles théories. Paris: Hermes Science.
Some cognitive "mechanisms"
Simplicity
- Analogy
setzen → setzte
lachen → lachte
Murena, P.-A., Al-Ghossein, M., Dessalles, J.-L. & Cornuéjols, A. (2020). Solving analogies on words based on minimal complexity transformation. IJCAI, 1848-1854.
Dessalles, J.-L. (2008). La pertinence et ses origines cognitives - Nouvelles théories. Paris: Hermes Science.
Some cognitive "mechanisms"
"CAN"
CAN: Conflict — Abduction — Negation
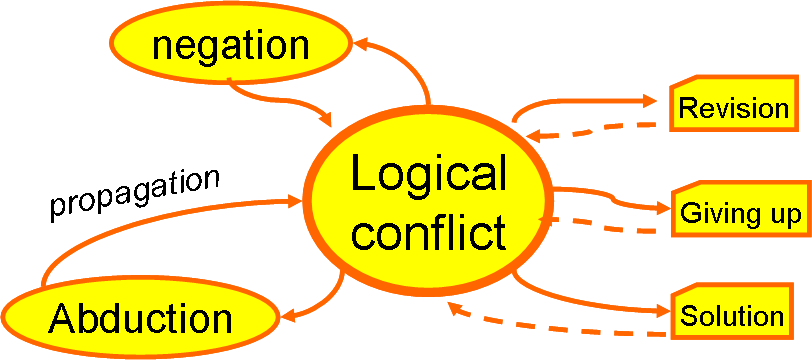
Dessalles, J.-L. (2016). A Cognitive Approach to Relevant Argument Generation. In M. Baldoni, C. Baroglio, F. Bex, T. D. Bui, F. Grasso & et al. (Eds.), Principles and Practice of Multi-Agent Systems, LNAI 9935, 3-15. Springer.
Should AI imitate cognitive mechanisms?
Future AI cannot rely exclusively on "canned" intelligence.


Should AI imitate cognitive mechanisms?
Future AI presupposes to perform
on-line computations.
to implement fundamental cognitive mechanisms
and execute them on the fly.
- syntactic processes
- aspect
- contrast
- simplicity
- CAN
- determination - relations - semantic linking . . .